Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Let’s say you’ve changed your home address — you’d leave a note for friends to find your new place, right? That’s pretty much what a redirect does on a website. So, what is a redirect in SEO? It’s simply a way to point both users and search engines from an old URL to a new one. And while it might sound technical, it’s a basic but powerful tool every site owner should know about.
Now, not all redirects are the same. There are different types of redirects in SEO, like the popular 301 redirect vs 302 redirect — and choosing the wrong one can actually hurt your rankings. That’s why it’s important to know how redirects affect SEO before making changes.
In this post, I’ll walk you through URL redirection explained in plain English. You’ll also get real advice on how to use redirects in SEO, learn redirect SEO best practices, and how to avoid the most common redirect mistakes in SEO. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to fix redirect issues in SEO the right way.
1. Introduction to URL Redirection Explained
URL redirection, also known as URL forwarding, is a process where one web page automatically sends users and search engines to a different web page. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a website’s structure, usability, and search engine optimization (SEO). Whether you’re changing your domain, fixing broken links, or merging content, understanding URL redirection explained properly helps keep your website healthy and search-friendly.
Redirection ensures that both users and search engines find the right content even if the original URL no longer exists. Without proper redirection, visitors may land on 404 error pages, damaging user experience and search rankings. Search engines, especially Google, use redirection signals to transfer ranking value from the old page to the new one, preserving your SEO efforts.
There are various types of redirects used depending on the situation, and knowing how each works is key to avoiding SEO issues. Implementing the correct redirect not only saves valuable link equity but also guides users smoothly through your website.
In this blog, we’ll explore what is a redirect in SEO, different types, their impact, and best practices. Proper URL redirection explained in this guide will help you make smart, SEO-friendly decisions for long-term success.
2. What is a Redirect in SEO?
A redirect in SEO refers to the process of forwarding both users and search engines from one URL to another. This is typically done when a webpage’s URL changes, is moved, or is deleted, ensuring that visitors still land on the right content. In the context of SEO, redirects help preserve your site’s visibility, authority, and overall user experience, making them a crucial element of website management.
Without redirects, visitors who land on a broken link or an outdated URL will encounter a 404 error, negatively impacting their experience and potentially causing a drop in search rankings. By implementing a redirect, search engines understand that the content has been moved, allowing them to pass on the ranking signals to the new page.
In SEO, redirects also help maintain the valuable link equity your pages have earned. For instance, when migrating from one domain to another or making structural changes, a well-implemented redirect helps transfer the SEO value from old pages to new ones. Understanding what is a redirect in SEO is essential for effective SEO strategy and ensures that your pages remain accessible to users and crawlers alike.
3. Types of Redirects in SEO
There are several types of redirects in SEO, each serving a different purpose depending on the situation. Understanding these redirects is crucial for managing website structure, maintaining SEO performance, and ensuring a smooth user experience.
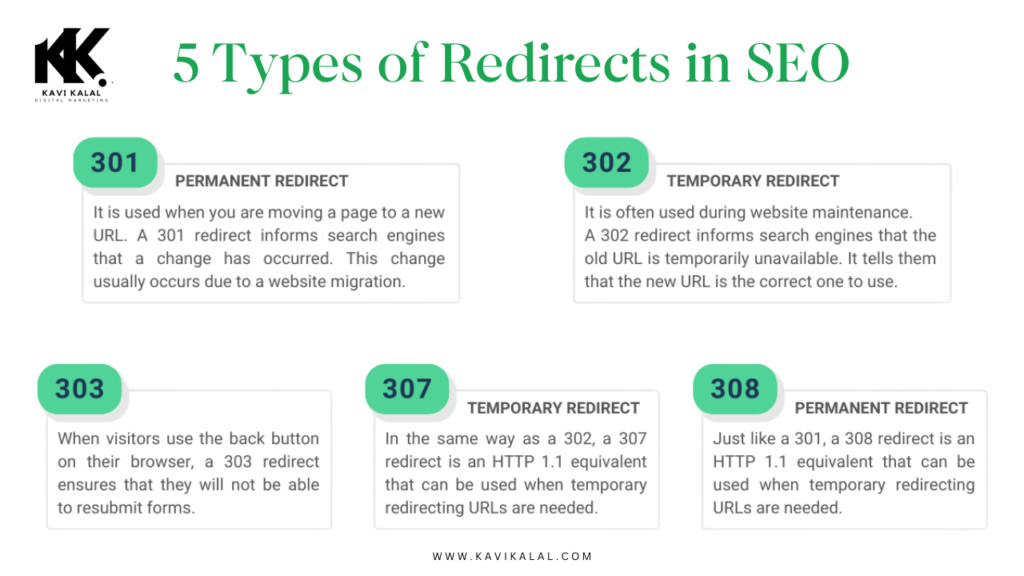
- 301 Redirect: This is a permanent redirect used when a page has been permanently moved to a new location. It passes most of the link equity to the new page, making it the best option for SEO when rebranding or restructuring a website. A 301 redirect is vital for preserving rankings and preventing broken links.
- 302 Redirect: Known as a temporary redirect, the 302 redirect is used when content is temporarily moved. Unlike the 301 redirect, a 302 redirect does not pass all of the link equity to the new page, which can affect SEO if used incorrectly.
- 307 Redirect: Similar to the 302, a 307 redirect is a temporary redirect but it’s used for HTTP/1.1 requests. This redirect also does not transfer link equity, so it should only be used for short-term changes.
- Meta Refresh Redirect: Often seen on landing pages, the meta refresh is a client-side redirect, meaning it can take a few seconds to execute. While not ideal for SEO, it’s useful for specific user interactions.
Each type of redirect in SEO plays a role in maintaining user experience and SEO integrity, and choosing the right one is essential for your website’s success.
4. 301 Redirect vs 302 Redirect: Key Differences
The difference between 301 redirect vs 302 redirect lies in how they impact SEO and how search engines treat them. Both are used to send visitors from one URL to another, but their underlying intentions and effects on rankings are quite different.
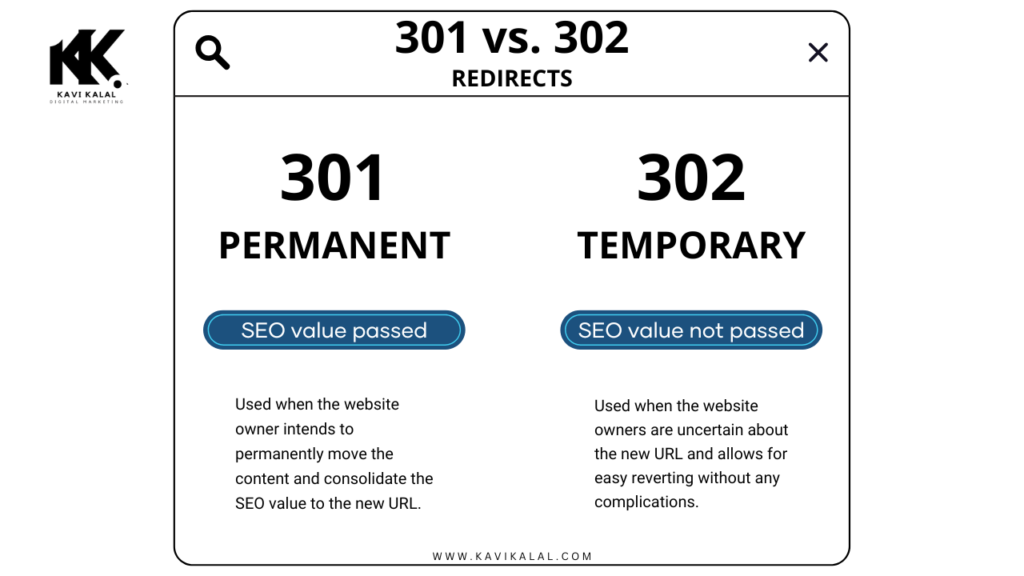
- 301 Redirect: A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect. It informs search engines that the original page has permanently moved to a new URL. This redirect passes almost all of the page’s link equity (also known as link juice) to the new page, which helps retain the SEO value and rankings of the original content. Using a 301 redirect is crucial when you’re making permanent changes to your website, such as changing domain names, merging content, or removing outdated pages.
- 302 Redirect: In contrast, a 302 redirect is temporary. It tells search engines that the move is only for a short period and that they should continue indexing the original page. Since it does not pass the same link equity as a 301 redirect, a 302 redirect is better suited for scenarios like seasonal promotions, temporary page changes, or testing purposes. However, using it for permanent moves can confuse search engines, possibly harming SEO performance.
Choosing the right redirect is critical for preserving SEO value. A 301 redirect should be used for permanent changes, while a 302 redirect should be reserved for temporary situations.
5. How Redirects Affect SEO: The Complete Breakdown
Redirects are an important element in SEO, with the ability to significantly impact how search engines crawl and rank your website. Properly implemented redirects ensure that users and search engines are directed to the correct page, preserving the user experience and SEO benefits. However, when misused, redirects can harm your site’s search engine optimization, causing issues with link equity, crawlability, and rankings.
One of the primary ways redirects affect SEO is by transferring link equity, or the value that search engines assign to a page based on backlinks. A 301 redirect, which is permanent, transfers most of the link equity from the old URL to the new one. This helps maintain search rankings and preserves the authority of the old page. Conversely, a 302 redirect signals to search engines that the move is temporary, which means the link equity is not fully transferred. This can lead to a loss in SEO value if used improperly for permanent changes.
Another aspect is crawlability. Redirects that lead to errors, such as redirect chains or loops, can cause search engines to miss important content or waste crawl budget. This can lead to indexing issues and lower search rankings. Furthermore, poorly executed redirects can create a frustrating user experience, leading to increased bounce rates and decreased engagement, which are negative signals for SEO.
In conclusion, while redirects are vital for website management, their use needs to be strategic to ensure that SEO performance is not compromised. Knowing how redirects affect SEO is key to preserving both rankings and user satisfaction. If you’re looking to master these techniques, enrolling in a digital marketing course can give you the hands-on knowledge you need.
6. How to Use Redirects in SEO Effectively
Understanding how to use redirects in SEO effectively is crucial for maintaining your website’s visibility and ensuring a smooth user experience. Redirects help guide users and search engines from outdated or removed URLs to relevant, updated pages. However, to protect your rankings, you must use the right type of redirect at the right time.
Start by identifying the purpose of the redirect. If a page is permanently removed or its URL has changed for good, always use a 301 redirect. This passes most of the original page’s SEO value to the new one, preserving rankings and link equity. If the change is only temporary, such as during testing or maintenance, a 302 redirect is more appropriate, as it tells search engines not to update their index permanently.
Avoid redirect chains, where one redirect leads to another. This confuses search engines and increases page load time, which can hurt SEO. Similarly, redirect loops should be fixed immediately, as they trap both users and crawlers in an endless cycle.
To ensure you’re using redirects correctly, audit your site regularly with tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console. By learning how to use redirects in SEO effectively, you can maintain rankings, avoid traffic loss, and provide a seamless experience for visitors and search engines alike.
7. SEO Impact of Redirects on Page Authority and Rankings
The SEO impact of redirects is often underestimated, yet it plays a vital role in maintaining and transferring page authority and search engine rankings. When URLs change or pages are deleted, setting up proper redirects ensures that the existing SEO value is not lost. If this process is ignored or poorly executed, it can lead to a drop in visibility, traffic, and authority.
A 301 redirect is the best method to preserve SEO value. When used correctly, it transfers the majority of a page’s authority (link juice) to the new URL. This helps search engines understand that the content has permanently moved and that the new page should inherit the old one’s ranking power. On the other hand, using a 302 redirect for permanent changes can confuse search engines. Since it’s considered temporary, it may not transfer full authority, negatively affecting rankings.
Redirect chains and loops can also dilute link equity, especially if there are multiple hops before reaching the final destination. Additionally, they can slow down page speed, another critical SEO factor. For best results, monitor your redirects consistently and make sure they lead directly to relevant, high-quality pages.
Understanding the SEO impact of redirects is essential for protecting your site’s authority and maintaining strong search engine rankings over time.
8. Redirect SEO Best Practices for Maximum Efficiency
To maximize your site’s performance and preserve rankings, it’s essential to follow the right redirect SEO best practices. Redirects should not only guide users and search engines efficiently but also maintain link equity and improve site structure. When implemented properly, they help avoid ranking losses and ensure a seamless browsing experience.
First, always use the appropriate type of redirect. Use 301 redirects for permanent changes, such as restructuring URLs or deleting outdated content. This passes the majority of SEO value to the new page. 302 redirects should be used only for temporary changes, as they don’t fully transfer link equity.
Avoid creating redirect chains—sequences of multiple redirects before reaching the final URL. These chains slow down page load times and reduce link authority. Similarly, fix any redirect loops, which can confuse search engines and prevent indexing.
Redirects should always point to relevant, high-quality pages. Sending users to unrelated or weak content can hurt your SEO and user experience. Also, regularly audit your redirects using tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or Google Search Console to identify broken links and improve performance.
By following these redirect SEO best practices, you can ensure that your redirects support—not sabotage—your site’s SEO strategy.
9. Common Redirect Mistakes in SEO to Avoid
Even a small error in setting up redirects can cause major SEO problems. Understanding the common redirect mistakes in SEO helps you prevent ranking drops, crawl issues, and lost traffic. Many websites unknowingly lose valuable link equity or confuse search engines due to poor redirect practices.
One of the most frequent mistakes is using the wrong type of redirect. For example, applying a 302 redirect for a permanent change means search engines might not pass link equity, leading to a decline in rankings. Always use a 301 redirect when a URL is permanently moved or removed.
Another major mistake is creating redirect chains, where one redirect leads to another, and then another. These chains slow down page loading, reduce link equity, and waste crawl budget. Similarly, redirect loops—where URLs endlessly redirect to one another—can prevent users and bots from accessing your content.
Redirecting all old URLs to the homepage is another bad practice. This confuses both users and search engines, especially when the content is no longer relevant.
Forgetting to update internal links after redirects is also common. This leads to unnecessary redirects and a poor user experience.
Avoiding these common redirect mistakes in SEO will keep your site technically sound, user-friendly, and search engine optimized.

10. How to Fix Redirect Issues in SEO Quickly and Safely
Redirect problems can damage your website’s search performance if not addressed promptly. Knowing how to fix redirect issues in SEO quickly and safely is essential for maintaining your rankings, ensuring smooth user journeys, and optimizing crawl efficiency. Fortunately, with the right tools and process, fixing these issues is straightforward.
Start by conducting a thorough site audit using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or Ahrefs. These platforms can identify broken redirects, chains, loops, and incorrect status codes. Once detected, prioritize fixing redirect chains by reducing multiple hops and sending traffic directly to the final destination page. This improves both speed and link authority.
Next, resolve redirect loops, which create endless cycles that confuse search engines and users. These are often caused by poor configuration and can be fixed by adjusting your .htaccess file or CMS settings.
Also, ensure that your 301 redirects are correctly used for permanent changes. Replace any incorrect 302 redirects with 301s if the move is not temporary. Don’t forget to update internal links so they point directly to the new URL rather than through a redirect.
By learning how to fix redirect issues in SEO, you protect your site’s structure, maintain authority, and deliver a better user experience.
11. Conclusion: Using Redirects Strategically for Long-Term SEO Success
When used strategically, redirects can play a powerful role in long-term SEO success. They help guide users and search engines to the right content, preserve page authority, and maintain search rankings during site changes. But to gain these benefits, you must understand how redirects work and use them wisely.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explained what redirects are, the types of redirects in SEO, and how redirects affect SEO performance. By now, you know that a 301 redirect should be used for permanent changes, while a 302 redirect is best for temporary situations. You also understand how improper use—like redirect chains or incorrect status codes—can damage SEO and user experience.
To achieve long-term results, follow redirect SEO best practices, regularly audit your site, and always align your redirects with your overall content and SEO goals. Avoid the common redirect mistakes in SEO, and act fast when issues appear by learning how to fix redirect issues in SEO efficiently.
In summary, mastering how to use redirects in SEO not only helps protect your rankings but also strengthens your site’s technical foundation. When done right, redirection becomes a long-term investment in your website’s health, authority, and success in search engine results.
FAQS
What is a redirect in SEO?
A redirect in SEO is a method used to automatically send users and search engines from one web page to another. It’s often applied when a webpage is removed, moved, or its URL structure is changed. Redirects help maintain traffic, preserve link equity, and avoid broken pages.
What are the main types of redirects in SEO?
There are several types of redirects in SEO, but the most commonly used are 301 (permanent), 302 (temporary), and 307 redirects, along with meta refresh redirects. Each redirect type signals a different intent to search engines and affects SEO performance differently.
What is the difference between a 301 and a 302 redirect?
A 301 redirect tells search engines that the page has moved permanently and passes most SEO authority to the new URL. A 302 redirect, however, is used for temporary changes and typically does not transfer full link equity. Using the right one is key for SEO.
Can redirects impact my website’s SEO rankings?
Yes, redirects can have a significant effect. Correctly implemented, they preserve link juice, improve user experience, and support crawling. But poor use of redirects can lead to slower site speed, lost traffic, and lower rankings.
How should I use redirects for best SEO results?
Use 301 redirects for permanent URL changes and avoid multiple redirect hops. Keep redirects direct, relevant, and up to date. Monitoring them with SEO tools ensures they continue to serve both users and search engines efficiently.
What redirect mistakes should I avoid in SEO?
Common errors include using the wrong redirect type, linking to unrelated pages, allowing redirect chains or loops, and not updating internal links. These issues can harm crawlability and SEO performance.
How can I identify and fix redirect issues safely?
Start with an audit using tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console. Fix broken or looping redirects, replace 302s with 301s for permanent changes, and clean up chains. Always test changes to make sure they work smoothly.